Scintillation properties of PSR B1133+16 measured with Very Long Baseline Interferometry
Ashley Stock
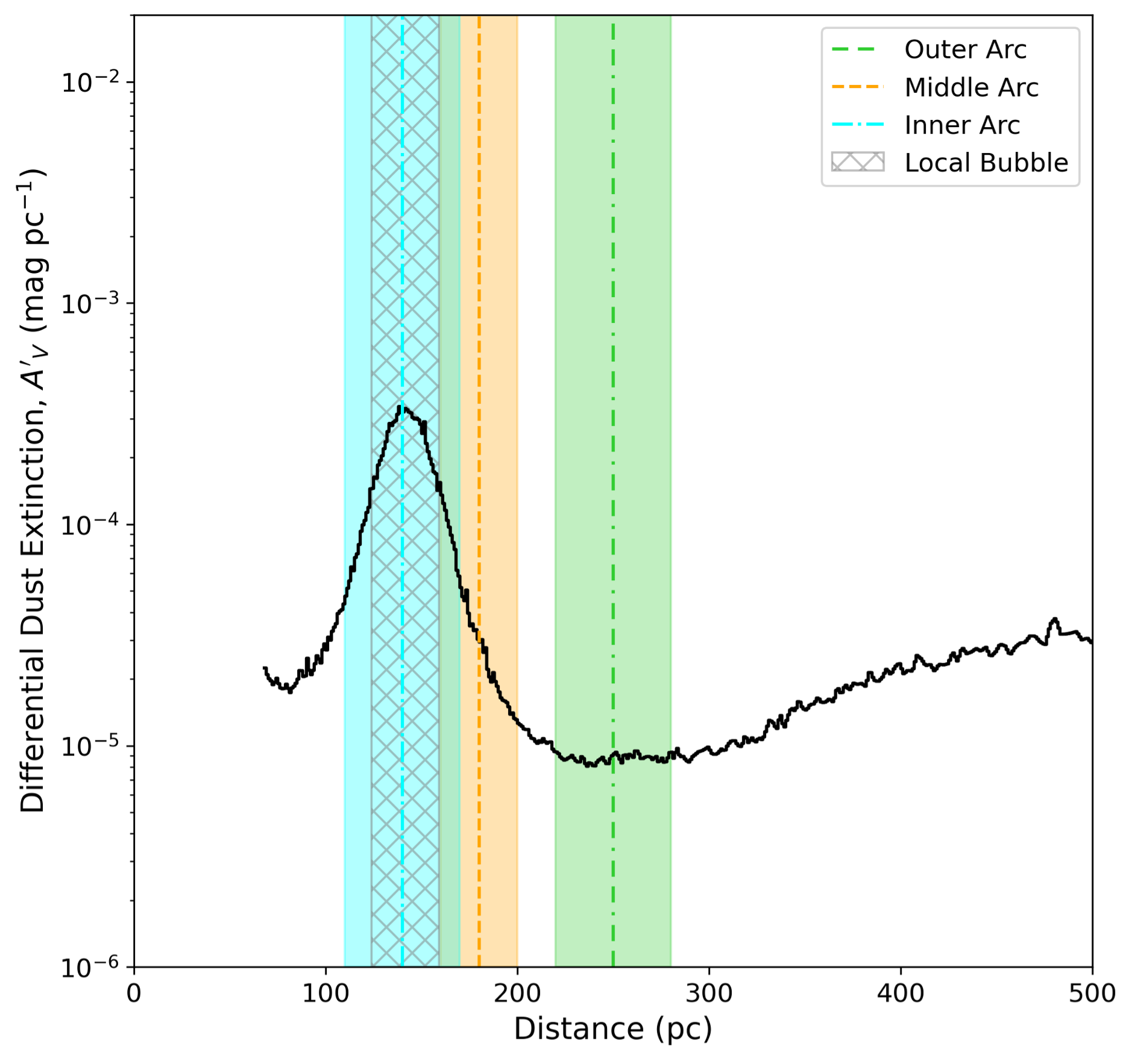
Previous measurements of the scintillation screens of PSR B1133+16 placed three of the screens at overlapping distances, suggesting an environment in the interstellar medium that is particularly conducive to forming scintillation screens. Our measurements are consistent within error but favour a typical separation for the screens of ~50 pc. Two of the screens are likely associated with the Local Bubble, with one of the screens coinciding with the peak in dust density from the wall of the Local Bubble while the other screen is located just outside of the wall.
Combining techniques from scintillation with VLBI allowed us to measure the properties of the scintillation screens simultaneously in a single epoch, unlike single dish measurements which typically require several observations over the course of a year. The phase information from VLBI gives the position of the scattered images with less assumptions about their distribution, making VLBI an incredibly powerful tool for better understanding pulsar scintillation.
Link to the paper:
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 992, Issue 2, id.192, 9 pp.
Contact:
Ashley Stock. Email: astock@swin.edu.au